Aircrack 2 3 Windows Living
In our ages, most of the providers give out protection in there wifi modem. Unfortunately most of these wifi boxes apply WEP crypting by default if we activate the wireless. It is likely known that this protection has passed deadline. Week and easily crackable. A small hour is enough to crack a 128 bytes WEP key ( packets capture + crack) and barely more for a 256 bytes key with aircrack. So I give to you a little tutorial that will help test out your wireless network, and most likely convince you to change to WPA crypting. Aircrack: To test the security of your network, we will need aircrack designed by Christophe Devine.
This program works under windows and linux, but some of the functionality are not available under windows (packet injection for example) That is why we will use a linux bootable cd OS:, this distribution is specialized in intrusion tests. Actually the is (in cases little) more up to date talking about wifi drivers and there utilisation is exactly the same. (These distribution are oriented in WEP cracking, but ubuntu or any other would to the work to) But not all the cards are supported, basically it depends of the chipset, here is a (compatible). This tutorial was realized with a (not G650 +!!!), fortunately My neighbour had a livebox (french wifi modem) and autorized me to crack his WEP on his network. He authorized it thinking I would not succeed. It turned out he was wrong, it took me approximately 2 hours to crack it.
For private property reasons, all the names of the networks ( ESSID) were masked except the ones from where the WEP was cracked, that was only partially hidden. The BSSID addresses (mac addresses) also have been partially censured, I only shown the first part of the MACS which correspond to the builder of the card. I repeat if you try to invade a network, you need the authorization from the owner, or you need to be the owner 1:// Whax: Now we are getting serious. So you can fully use your card we will use a live cd of linux (me too, I don’t know anything about the penguin) Get the WHAX distribution here: Download Whax: ou MAJ: there are new distributions of live cds specialized in monitoring wifi, like troppix and backtrack that are as good or even better. You can found all those distro on The functionality is basically identical. Indeed they all include aircrack and airodump/aireplay. Burn the distrib on a nice cd and put it aside for 2 seconds.
2 3 Bts
On the side I suggest creating a FAT32 partition of 2 or 3 gigs. The advantage of FAT32 is that it is readable by windows and linux.
That partition will be used to stock packets captured and the different files necessary to crack the key. That partition is not required, but it is recommended especially if you have low RAM capacity since the capture files would be stock in RAM (no partition). Also when you have a FAT32 partition you can stop the computer and restart monitoring without losing anything. WATCH OUT, YOUR PARTITION WILL NOT HAVE THE SAME NAME UNDER LINUX, SO PLACE A FILE THAT YOU WILL RECOGNIZED IN IT. After booting on Whax you will end up on a login screen (for troppix you only need to chose video card + keyboard language + resolution) The login is Root and the password is toor, to start the graphical interface, type startx ( you need to type stqrtx since the keyboard will be English, HELL if your reading this ur English =/ so if your stuck with a French keyboard, GET A CLUE You will then end up on the. Also, open a shell: The interface is KDE so it is easy to get used to.
Aircrack-ng is a complete suite of tools to assess WiFi network security. It works primarily Linux but also Windows, OS X, FreeBSD, OpenBSD, NetBSD.
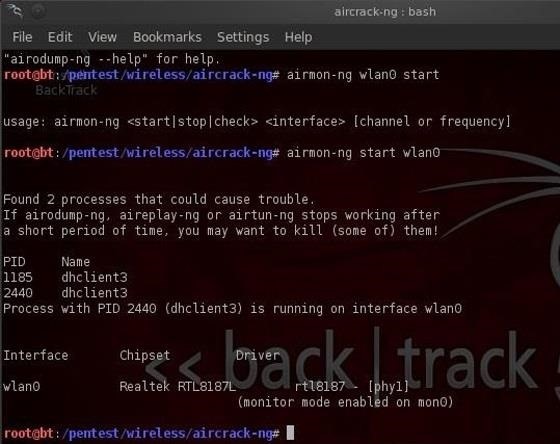
(simple click) Then type in 'airmon.sh'to detect the interfaces and select the one that you want to use with the command 'airmon.sh start « wifi interface » ' (note that there are no brackets, all though there will be used throughout this whole tutorial) Here you can see that the card is correctly recognized and that the monitor mode is directly activated. The monitor mode lets us capture packets transiting even the ones that aren’t directed to you.;) And if you already use a linux distribution and you only need to install the aircrack suite: 2:// Airodump: Detailed use of and Now we will start to scan the wireless networks with airodump (part of the aircrack suite). We type in the console: ' airodump interface name name of the output file channel to scan' To chose to scan all the channels type in 0 You can add the parameter 1 at the end, to modify the extension of the output file to.ivs rather then.cap, that advantage is that the file does not contain all the packets info but only the IVs, the size is more convenient. « airodump ath0 out 0 1 » You need to chose this method if you did not create a FAT32 partition, otherwise you can have a crash (if not enought RAM)!!! If you created a FAT32 partition, you should prefer the.cap If you created a FAT32 partition you need to place yourself in that partition Do « cd. » to go back to the root.
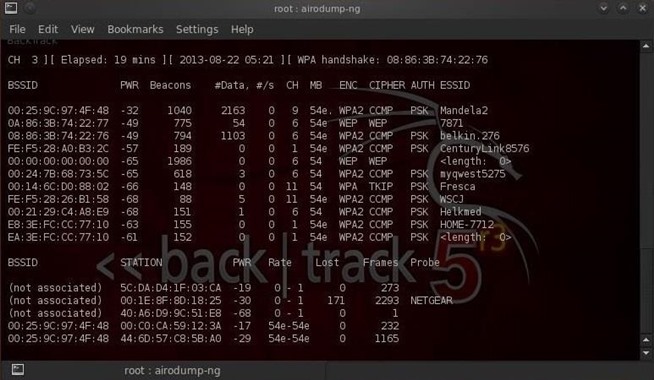
Then 'cd mnt' to open the folder that corresponds to the “ my computer “ under windows. For my part I type in « cd. » then « cd mnt/hda6 » We then find this once airodump launched: I am in a student residence so there are a lot of people. The BSSID column corresponds to the Mac addresses of the access points (AP) The ESSID colujmn corresponds to the name of the network (MyWifiNetworw, Wanadoo-xxxx.) The first part corresponds to the access points and the second part to the stations ( the computers that are logged in) The column that interests us is the one that has IVs, those are the files that will allow us to crack the WEP keys. Here the AP of my friend is the only one where the ESSID is not totally masked. For better performances in the capture of packets, we re lunch airodump chosing only the canal where the AP is (here is 10) « airodump ath0 out 10 » To stop the capture and enter commands do Ctrl + C You are also obligated to stop the capture if you want to copy a mac address since the screen refreshes. To copy something simply select with the mouse and right click copy.
Idem to paste or use Shift+insert. For more details on airodump simply type in airodump in the console and the help will appear. There we have stations and one that is connected to the AP that interests us. BINGO cause the access points have sometimes (and it’s the case of freeboxes) a mac filter called ( mode association) and for aireplay we need that mac address, actually we are acting as if we were that computer to have the access to the AP. As soon as we start getting IVs airodump tells us what type of crypting it is: WEP WPA or OPN.
Now we know that the crypting is WEP, that a station is presently logged, and there is traffic (350 packets for the station in not a lot of time) we are going to launch aireplay, a packet injector to accelerate the traffic and stimulate the IVs sent. You need to know that to crack a WEP key of a wifi network, it is more convenient that there is a minimum of traffic. By experience the IVs capture is a lot faster, and also they need to be diversified since the crack will need less IVs’s. For example here there is traffic, but unfortunately there wasn’t any after so I had to capt a lot of IVs before finding the key. 3:// Aireplay: In detail in the Just like airodump, aireplay is part of aircrack 3.1:// Fake authentication See the To launch aireplay open another console in the same screen with the help of the little icon on top left. You can also rename it with a right click. We launch aireplay once without worrying about the bssid of the station: The parameters are: “ aireplay -1 0 –e Essid -a Bssid of the AP –b bssid of the AP –h bssid of the station interface ” ' -1 0' corresponds to an attack by fake authentication, the zero is the delay that we authorize for the answer to come in.
Here we can see that if we place a dummy mac address the AP refuses us, but if we put the BSSID that airodump gives us it works. Some of the AP don’t have any filtering of MAC addresses and you can put any MAC address. Once you have “ association successful “ it is a first victory, basically you are accepted by the access point wifi. It is possible that if you don’t capt the signal (if the power is low ) that the authentication is successful and the association is not immediate. Here the example is small but you can easily have 40 lines:-S Here is a small scheme that will show you the relations between the parameters of aireplay and the capture of airodump: The association is not really reliable and if it fails, you can still go through the next step. 3.2:// Packet Injection: In detail Once the association is good, we relaunch aireplay changing some of the parameters.
You need to change the first parameter by “-3” that corresponds to an attack by packet injection. Then you need to add the parameter “-x” following a value that corresponds to the number of packets per seconds that aireplay will send. Here it is 600, Depending on the AP signal strength modify the parameter.
Also, following the capture file (airodump) add in the parameter –r. This parameter indicates in which file read to see if there are ARP’s inside. The ARPS are what will allow us to influence the traffic.
DON’T FORGET TO PLACE YOURSELF IN THE SAME DIRECTORY To avoid to type it all, since the syntax is basically the same then the parameter -1 press the up arrow key to have what you have previously entered. Aireplay saves ARPS in a file that he makes every time it is launched. It is underlined in the picture.
That file finds itself in the folder where you lauched aireplay It is that file that you then put in the parameter –r if you got ARPS, the ARPS are obtained by reading the file indicated but also by listening the the network, like airodump does. Here, we can see that we have an arp. As soon as we get an ARP aireplay starts sending packets. And normaly if everything is going well, the IVS grow.
Fraction Calculator
And it is the case, they are growing:D: At the sime time, the arps also go up: Au maximum aireplay garde 1024 ARP. To give you an idea of the speed for capting IVs’s I did some print full screen, look at the clock.
4:// Aircrack: In detail in the Know that you need approximately 300k IVs for a 64 byte WEP key and about 1 mil for a 128 WEP key, it is pretty fast. You should launch Aircrack once you have 300k and if you suppose that the key can be e64 bytes(you should know, its your network) For that in the parameters of aircrack, you only need to add –n 64, and aircrack will try to crack the WEP key as if it was a 64 bytes WEP key, even if it is a 128 bytes key. Personaly this tuto aimed a 128 bytes key (livebox) so I don’t send it with 64, But since I have approximately 700k ivs, I can start to launch aircrack while the capture of packets is still going on with airodump. Open a new shell and launch aircrack. Don’t forget to place yourself in the folder containing the files of airodump, if you have created a FAT32 partition “aircrack –x -0 nameofthecapturefile” The Parameter –x stops the bruteforcing of the last 2 bytes, it accelerates the crack (normally) The parameter -0 puts aircrack in color and it’s the only thing it does, but MAN doesn’t it look cool when some ones cracking and you see the matrix like coding in his screen.
Finaly the last parameter is the name of the capture file of airoduimp, you can also use the syntax “.cap “ and “.ivs “ to open all the files.cap and.ivs. “aircrack –x -0.cap.IVs “ Once we have launched aircrack, it shows all the networks that it saw, the crypting, the number of IVs corresponding. You then only need to chose the right number and to launch aircrack now it starts to crack the key: The capture of airodump keeps going while the aircrack increments automatically all the new IVs and uses them to crack the key. Now the only thing you need to do is let it run and the WEP key should show in red, if the crack works.
Basically it works statically with a vote system counting the Ivs’s, more a byte has votes compared to the other bytes of the same row, more it has chances to be good. Unfortunatly for me, the crack dint work even though I had more then enough IVs’s I believe it is because there was barely any traffic, maybe even none. The only thing to do is get more IVs’s When you recapture IVs’s, the best thing to do is to wait for the station, get new ARP’s and let Airodump run. Personally I let airodump run and relaunched an aireplay removing the –r parameter so that it gets new ARP’s. So when the station reconnects new ARP’s are in movement and I capture them right away re injecting, it’s the best method.
If your not able to capture ARP let the capture run as long as possible and when a station is connected try an it should stimulate the ARP emission. “ aireplay -0 + the usually ESSID and BSSID parameters ” So I left and when I came back I had around 2.6 mil IVs’s, more then enough. Relaunching aircrack: Bingo!!!! We can see that comparing the 2 images the one where the attack failed and the one where it worked, we find basically the same numbers, which means we only needed new IVs’s.